he overwhelming competition in the FMCG industry, also known as Fast-Moving Consumer Goods, has put players in a ‘survival of the fittest’ situation. In the present scenario, it is not just about tailor-making the products to suit the customers’ needs, but the deciding factor of your success in the market is the ability to reach customers before your competitors do. Furthermore, emerging markets have opened up new doors of opportunity for FMCG companies. So, it has become crucial for businesses to identify different supply chain strategies to reach out to these customer segments effectively. Also, consumer goods companies are increasingly embracing globalization. This has not only sparked complexity in the supply chain and other processes but has also bloated inventory levels, depleted the working capital requirements for new products, and reduced margins.
There are several issues that FMCG companies need to address to align the current demand and supply requirements. Here, we examine some of the critical supply chain challenges that players dealing in consumer goods need to beat for the smooth flow of operations
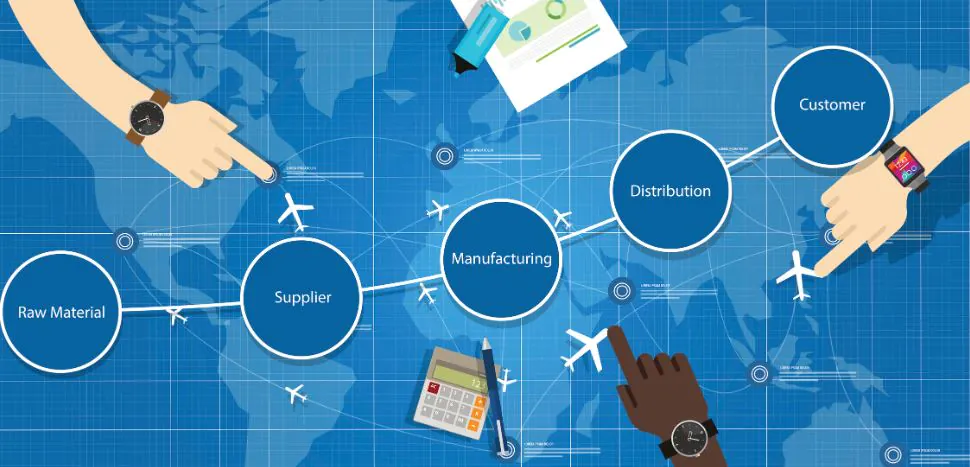
Components of an FMCG Supply Chain
-
Supply of Raw MaterialsSourcing goods from reliable suppliers to ensure timely delivery and favorable pricing conditions.
-
In-plant LogisticsManaging the transfer of goods within the production process to ensure a smooth workflow.
-
StorageOrganizing production schedules, testing items for quality, and preparing them for distribution.
-
TransportationMoving products from warehouses to distribution centers or retailers.
-
Delivery / DistributionEnsuring products reach retailers or consumers efficiently.
Top Supply Chain Challenges in FMCG
Fierce Competition and Speed of Delivery: The FMCG industry is highly competitive, with companies needing to deliver products quickly to stay ahead of competitors. This requires efficient logistics and distribution systems to ensure timely availability across all channels.
Supply Chain Sourcing: Ensuring the availability of raw materials and packaging from the right suppliers at the right time is a significant challenge. Building strong relationships with suppliers and having backup suppliers is crucial to mitigate disruptions.
Product Cost Concerns: Rising inflation and fluctuating raw material costs pose significant challenges, affecting product pricing strategies and profit margins. Companies must balance cost-effectiveness with maintaining product quality and customer value.
Inadequate Infrastructure: Poor infrastructure, such as bad roads and inadequate transportation systems, increases logistics costs and hinders operational efficiency. Investing in infrastructure or optimizing logistics routes can help mitigate these issues.
Regulatory Compliance: FMCG companies must navigate complex global regulations, including trade compliance, product safety standards, and environmental regulations. Non-compliance can lead to severe financial and reputational consequences.
Complexity and Volatility: The FMCG supply chain is complex due to numerous distribution centers, factories, and SKUs, making it vulnerable to disruptions. Volatility in demand due to trends and seasonality requires agile supply chain management to prevent stockouts or overstocks.
Maintaining Product Quality Across Markets: Variations in raw material availability and production standards across regions can affect product consistency. Standardizing production processes and implementing quality control measures are essential to maintain a uniform brand experience globally.
Solutions for FMCG Supply Chain Challenges
Enhance Supply Chain Visibility
Implement Supply Chain Visibility Platforms: These platforms provide real-time data on every stage of the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products. This allows companies to anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize stock levels, and respond promptly to market shifts.
Benefits: Improved operational flexibility, reduced risk of stockouts, and increased customer satisfaction.
Adopt Agile Supply Chain Practices
Optimize Distribution Networks: Enhance pick-and-pack services to increase responsiveness and flexibility. This involves streamlining logistics operations to quickly adapt to changes in demand or supply disruptions.
Benefits: Faster response times to market changes and unexpected disruptions.
Build Cooperative Supplier Relationships
Develop Contingency Plans: Share forecasts and maintain constant communication with suppliers to reduce the impact of supply chain disruptions.
Benefits: Stronger supplier relationships can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Leverage Data-Driven Decision Making
Utilize Advanced Analytics: Implement Inventory Management System Software to make informed decisions based on accurate demand forecasts and inventory optimization.
Benefits: Predictive analytics can adjust production and inventory levels in response to changing demand patterns.
Conduct Risk Assessments and Scenario Planning
Identify Potential Risks: Develop preventive measures by modeling different scenarios to evaluate the impact of risks.
Benefits: Proactive risk management helps minimize disruptions and maintain operational efficiency.
Invest in Infrastructure and Technology
Automate Warehouses: Use automated systems to optimize storage and transportation, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Benefits: Enhanced operational efficiency and reduced logistics costs.
Emphasize Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Integrate Sustainable Practices: Limit waste, ensure fair work practices, reduce carbon emissions, and source raw materials responsibly.
Benefits: Improved company reputation and appeal to eco-aware customers.
Collaborate with Retailers and Customers
Coordinated Planning: Share data and inventory with retailers to match supply chain operations to consumer demand.
Benefits: Ensures product availability and enhances customer satisfaction.
Innovate with Technology
Use AI, Blockchain, and IoT: Enhance demand forecasting, inventory control, and product traceability.
Benefits: Improved supply chain visibility, efficiency, and product authenticity.
Conclusion
FMCG companies face numerous supply chain challenges, from competition and sourcing to regulatory compliance. To overcome these, they must adopt agile practices, enhance supply chain visibility, and leverage data-driven decision-making. By investing in technology and fostering collaborative relationships with suppliers and retailers, companies can improve operational efficiency, reduce risks, and enhance customer satisfaction. This strategic approach enables FMCG businesses to maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.