The power sector is undergoing a gradual digital revolution, with data collection and exchange growing exponentially, presenting both digital threats and valuable opportunities in the industry. Comprising energy suppliers and distributors in electric, nuclear, coal, wind, solar, and natural gas technologies, the power sector faces variations across regions but maintains a similar operational structure worldwide. Responses of power companies depend on regulatory environments, geographical locations, asset portfolios, dynamic customer demands, economic maturity, and required technology adoption levels. Despite differing visions for the global power sector’s future, one undeniable truth prevails – the industry stands on the brink of massive change.
Conducting a SWOT analysis of the power sector reveals the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the industry, both internally and externally.
Request a demo to understand how market intelligence can help you
Weakness
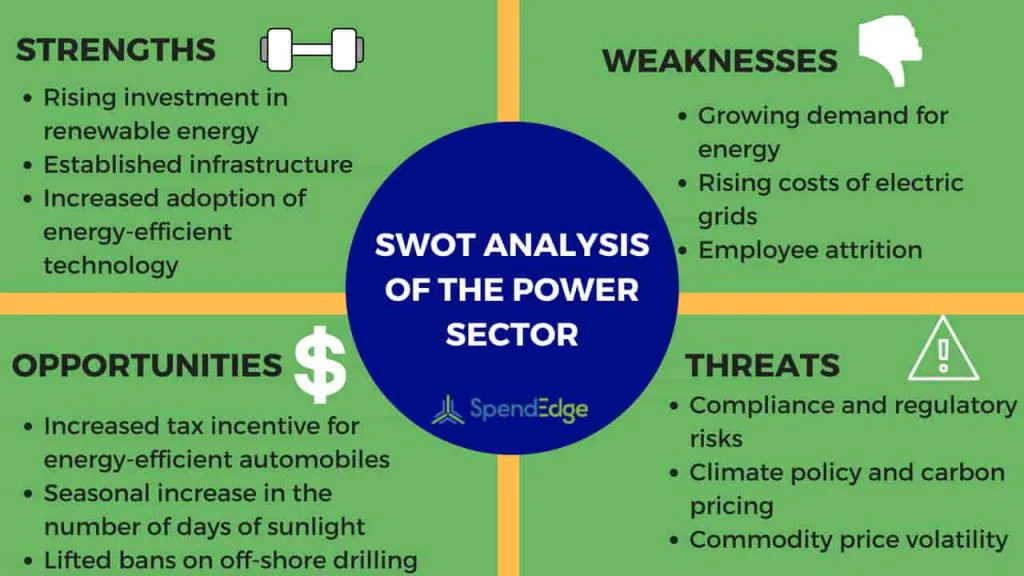
In the SWOT analysis, weaknesses highlight low-performing or inefficient features within the industry. The global population surge and increasing industrialization in developing nations have intensified the demand for energy to unprecedented levels. Common weaknesses for companies in the power sector include:
- Coping with the growing demand for energy
- Managing the rising costs of electric grids
- Addressing employee attrition challenges
Opportunities
Leveraging a SWOT analysis, power sector companies can identify growth opportunities. The escalating rate of data collection and exchange opens new avenues in the energy industry. Opportunities span the entire power-industry value chain, from generation to customer relationship management, including:
- Capitalizing on increased tax incentives for energy-efficient automobiles
- Utilizing seasonal increases in the number of days of sunlight
- Exploring opportunities arising from lifted bans on offshore drilling
Threats
SWOT analysis identifies external threats potentially hazardous to the power sector’s continued growth, often beyond the control of companies. Presently, due to the sector’s social and economic impact, companies are under constant pressure to enhance efficiency and attain greater cost competitiveness. Key threats facing power sector companies encompass:
- Navigating compliance and regulatory risks
- Managing uncertainty in climate policy and carbon pricing
- Mitigating commodity price volatility
Renewable Energy:
- Renewable energy assets contribute significantly to the power sector’s transition.
- Various countries have different standings in terms of renewable energy adoption.
- The prospects for renewable energy involve a detailed analysis of key resources and power generation methods.
- Global leaders are emerging in green power production.
- A clear picture of each country’s renewable future helps outline the path towards carbon neutralization.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Renewables:
- The benefits of renewables include economic growth, technological advancements, and sustainable development.
- Drawbacks encompass higher upfront costs, geographic limitations, and intermittency.
Energy Mix and Policy Implications:
- The energy mix involves balancing various sources for sustained growth.
- Policy implications at governmental levels are crucial for the successful integration of renewable energy.
SWOT Analysis and Growth Factors:
- Conducting a SWOT analysis helps identify growth factors and dominant factors within the renewable energy sector.
- The utilization of renewable sources depends on multi-level governance, requiring effective communication and right actions.
- Reducing energy imports is a key focus, raising research questions regarding the potential benefits.
Electrical Power Sector and Transition Challenges:
- The electrical power sector plays a vital role in economic growth and development.
- Global demand for decarbonization is driving a shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources.
- Electrification impacts transport, heating, and overall global warming and climate change concerns.
- The electricity consumption pattern is changing with the massive deployment of renewable energy.
Market Dynamics and Technological Advancements:
- Market dynamics include the impact of renewables on utility companies, grid stability, and overall energy transition.
- Technological advancements in energy storage, smart grids, and energy efficiency drive the shift towards renewables.
Policy Frameworks and Innovation:
- Government regulations, investment, research and development, and innovation play pivotal roles in economic efficiency and environmental conservation.
- Successful renewable energy integration requires robust policy frameworks, fostering a sustainable business model.
Grid Modernization and Distributed Energy Resources:
- Grid modernization is essential for accommodating distributed energy resources and ensuring grid reliability.
- The environmental impact, economic benefits, and job creation are significant outcomes of grid modernization.
Energy Equity and Electromobility:
- Achieving energy equity involves considerations of social responsibility, affordability, and public awareness.
- Electromobility contributes to achieving carbon-neutral goals, with carbon pricing and international cooperation playing crucial roles.
Digitalization and Energy Trade:
- Digitalization is transforming the energy sector, influencing energy trade, and fostering sustainable infrastructure and climate resilience.
- Green technologies and sustainable urban planning are integral to energy governance and green finance.
To know more about how a comprehensive SWOT analysis can help your business




